MIST: Multiple Instance Self-Training Framework for Video Anomaly Detection
Published in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021
Recommended citation form:
Jia-Chang Feng, Fa-Ting Hong and Wei-Shi Zheng. “MIST: Multiple Instance Self-Training Framework for Video Anomaly Detection, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2021.
Brief Biography
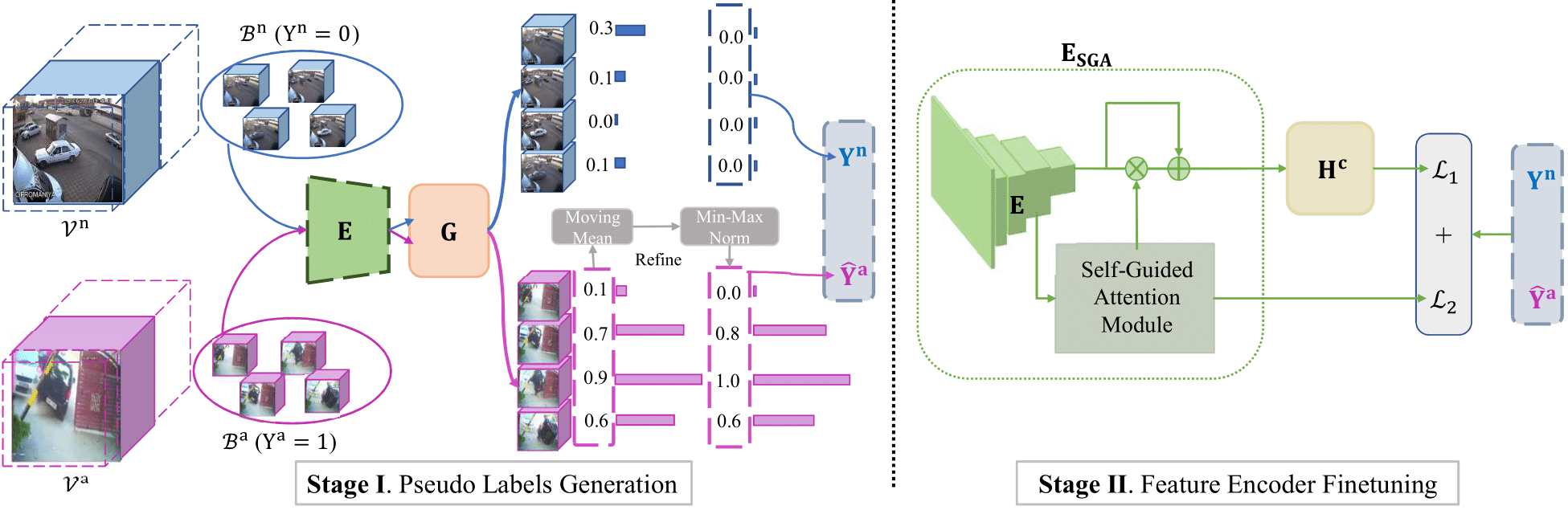
Weakly supervised video anomaly detection (WS-VAD) is to distinguish anomalies from normal events based on discriminative representations. Most existing works are limited in insufficient video representations. In this work, we develop a multiple instance self-training framework (MIST)to efficiently refine task-specific discriminative representations with only video-level annotations. In particular, MIST is composed of 1) a multiple instance pseudo label generator, which adapts a sparse continuous sampling strategy to produce more reliable clip-level pseudo labels, and 2) a self-guided attention boosted feature encoder that aims to automatically focus on anomalous regions in frames while extracting task-specific representations. Moreover, we adopt a self-training scheme to optimize both components and finally obtain a task-specific feature encoder. Extensive experiments on two public datasets demonstrate the efficacy of our method, and our method performs comparably to or even better than existing supervised and weakly supervised methods, specifically obtaining a frame-level AUC 94.83% on ShanghaiTech.
弱监督视频异常检测是一种基于可分特征将异常从正常事件中检测出来的任务。然而,大多数现有工作受限于不充分的特征表示。本工作中,我们提出了多示例自训练的框架(MIST),该框架仅使用视频级别标签,高效地优化任务相关的特征表示。特别地,MIST包括了(1)一个多示例学习的伪类标生成器,它采用了稀疏连续采样策略来产生更加可信的伪类标;(2)一个自引导注意力模块增强的特征提取器,用以在特征提取过程中使提取器更关注异常区域。另外,我们采用了自训练的方法来优化这两个部件,并最终得到一个任务特定的特征提取器。我们在两个公开数据集上做了大量实验,这些实验结果证明了我们方法的有效性,而且本方法的性能与现有的有监督和弱监督方法相当甚至更好,特别是在ShanghaiTech数据集上,本方法获得了94.83%的帧级别AUC分数。
Experimental Results
We have deployed extensive experiments on UCF-Crime and ShanghaiTech dataset, and outperforms other methods under the same setting.
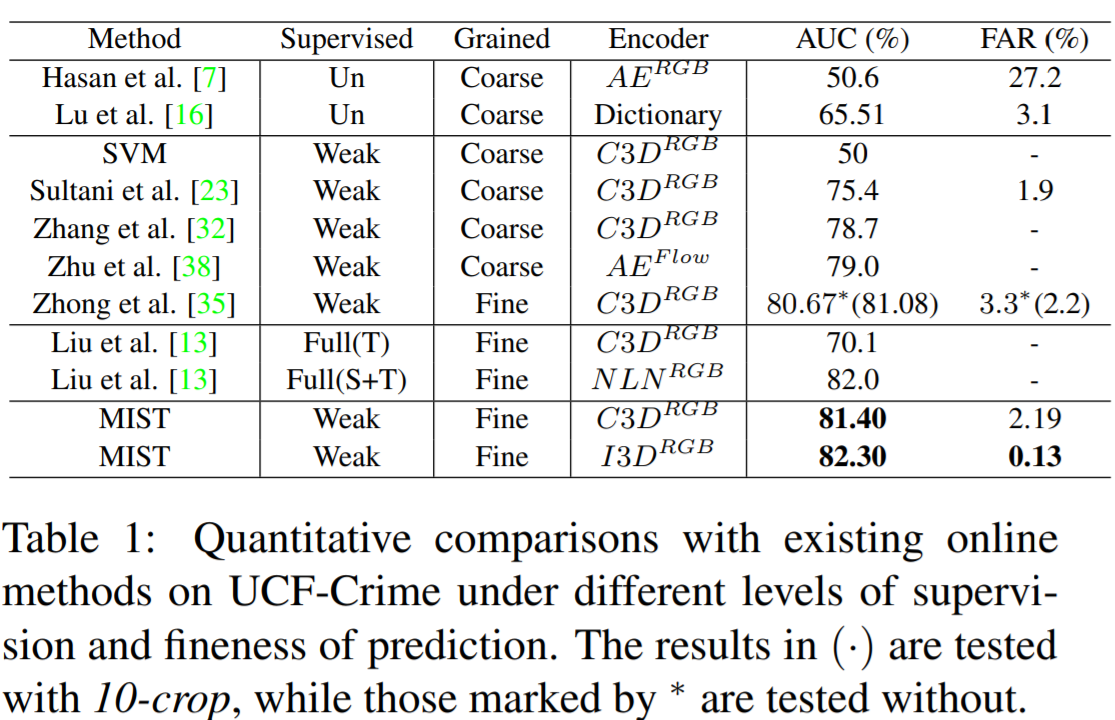
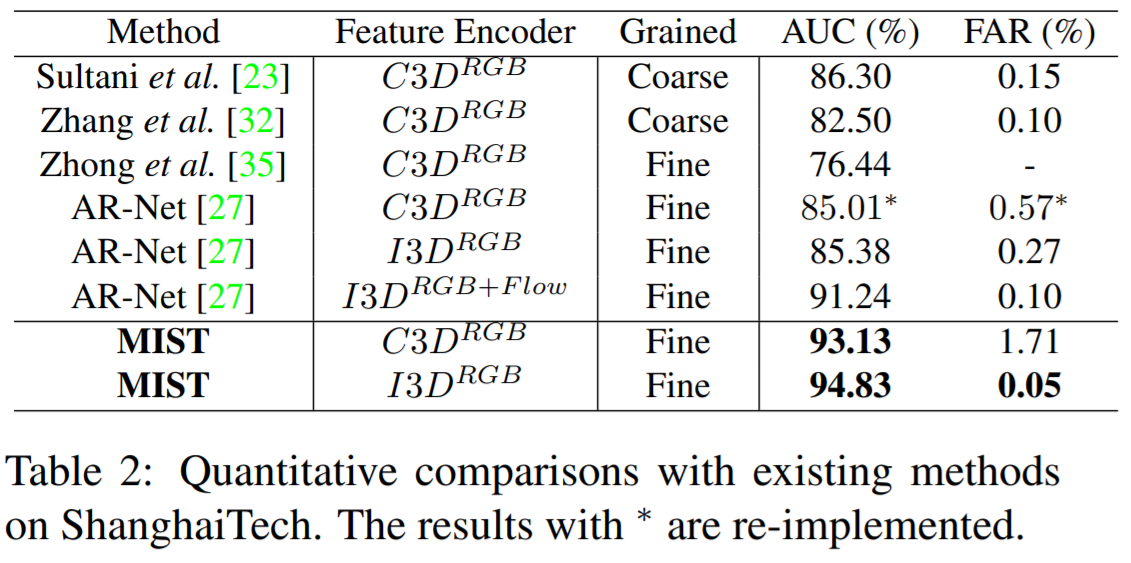
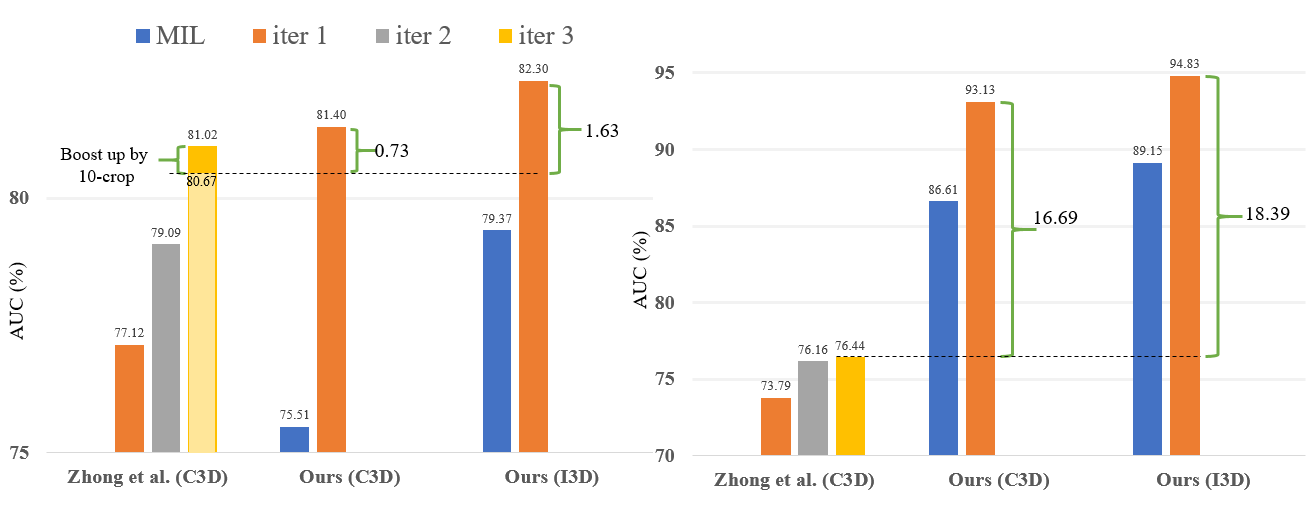
Comparison with previous encoder-based method [Zhong .et al, CVPR 2019] as below, the left of which are the results of UCF-Crime while the right are those of ShanghaiTech.
Visualization
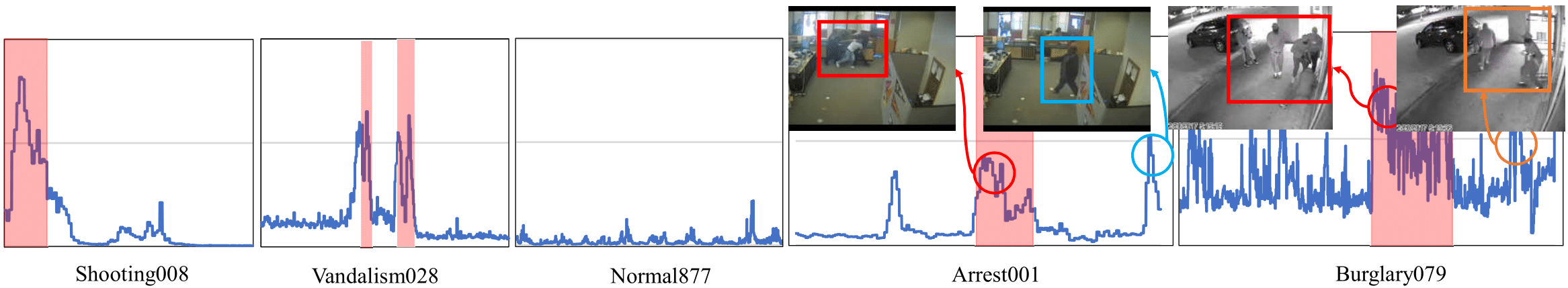
Visualization of the testing results on UCF-Crime (better viewed in color). The red blocks in the graphs are temporal ground truths of anomalous events. The orange circle shows the wrongly labeled ground truth, the blue circle indicates the wrongly predicted clip, and the red cricle indicates the correctly predicted clip.
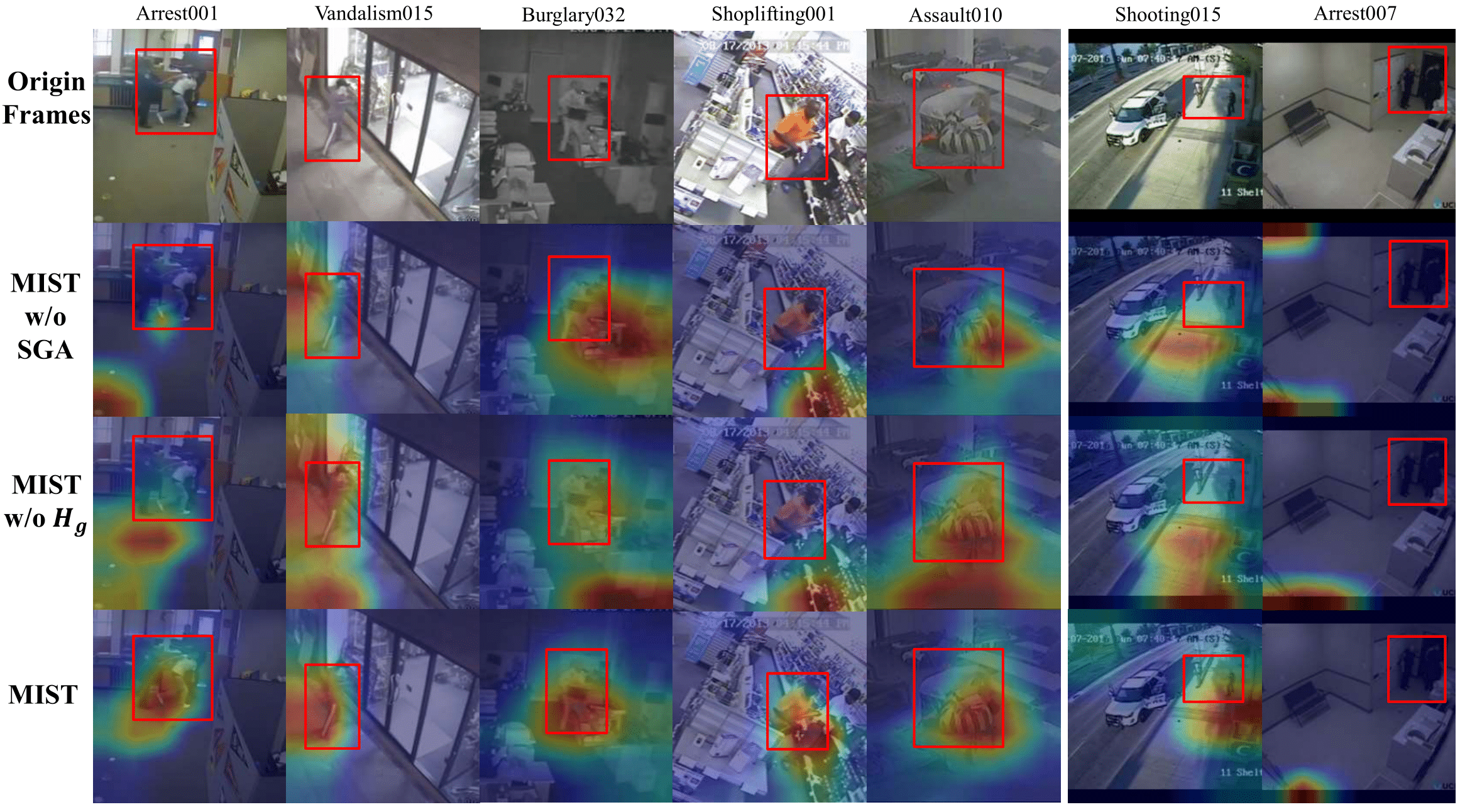
More spatial anomaly activation maps visualization on UCF-Crime. The left 5 columns of the graphs are the successful results while the right 2 columns are the failures.
The demo video is on Youtube, if you could not load it, you can clip here to watch the video.
Video Presentation
The video is on Youtube, if you could not open it, you can clip here to watch the video.
It’s recommended to turn on the caption.
Paper Download paper here
Poster Download poster here
PCSIG-GuangDong Talk Download PPT here , Watch Video here